Randy Jacobs, M.D. Patient Education
To return to the Patient Education page and read more articles, click here.

Atypical Mole
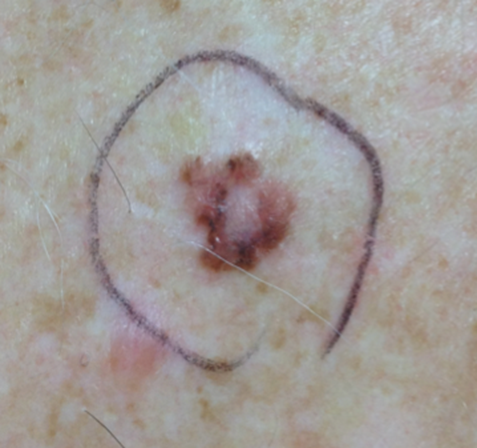
What Is An Atypical Mole? Dermatologists often refer to an atypical mole as a “dysplastic nevus.” Dysplastic – Refers to an alteration in size, shape, and cell organization. Nevus (pl. nevi) – Refers to a Mole, and Moles can be atypical, or dysplastic, due to variations in size, shape, or color. Dysplastic nevi are usually larger than benign moles, have indistinct borders, and range in color from tan to dark brown to black. Dysplastic moles can begin to appear on the skin by age 5, and are increased, in some people, by the sun. Interestingly, for some people, the sun causes freckles. However, in other people, the sun can cause moles. Thus, some people are “freckle makers’” and some people are “mole makers.” Dysplastic nevus syndrome is a condition that runs in families with family members who have many atypical moles. Dysplastic nevi also indicate an increased risk for developing melanoma, and this risk increases when: • There is a family history of melanoma • There is a family history of dysplastic nevus syndrome • Numerous dysplastic nevi are present • The skin is fair & heavily freckled due to excessive sun exposure
Some people ask that their atypical moles be mapped by photos. Dr. Jacobs believes that, if a mole looks bad enough to photograph, rather than photography, the mole should just be biopsied for microscopic evaluation. Yes, a biopsy can leave a small scar, but, removal of an atypical nevus is the best way to prevent melanoma.
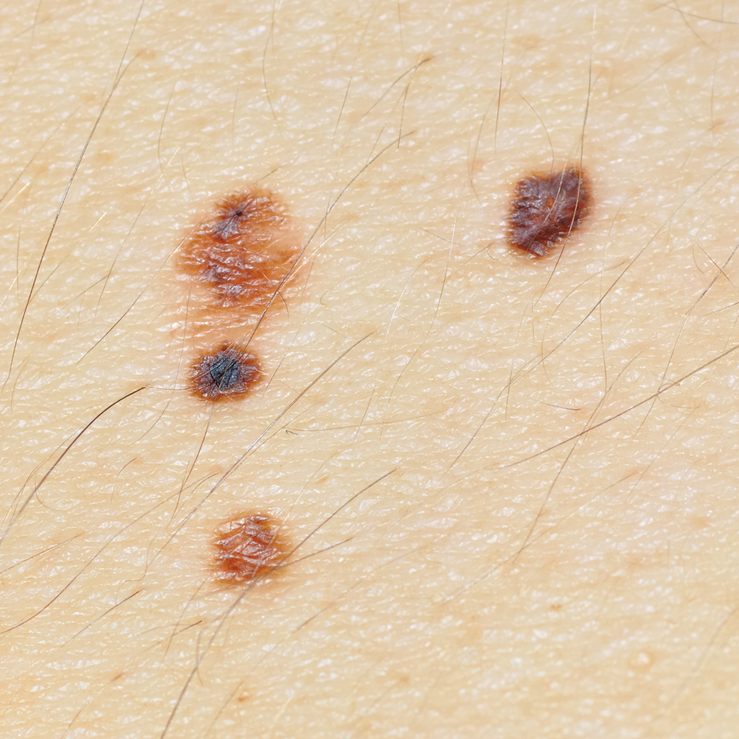
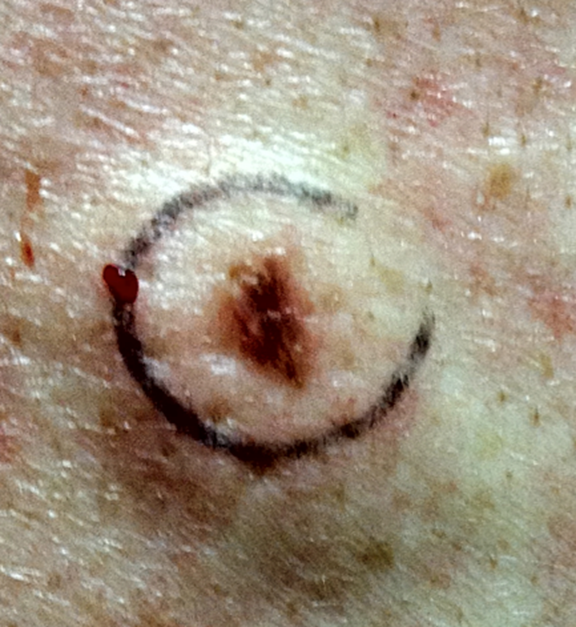
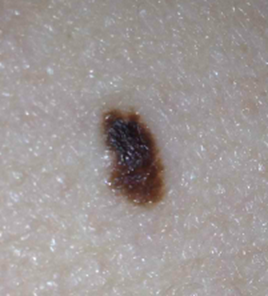
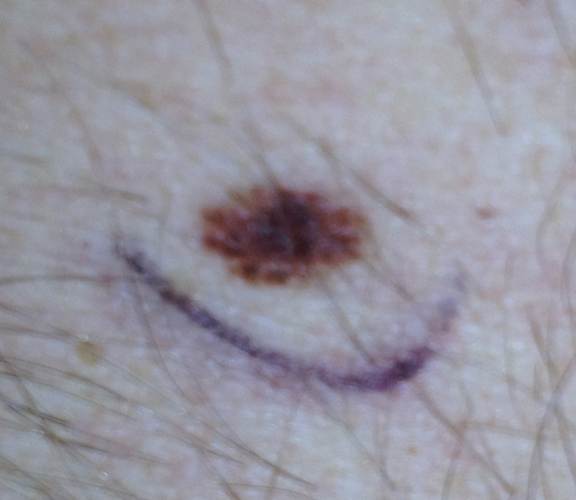
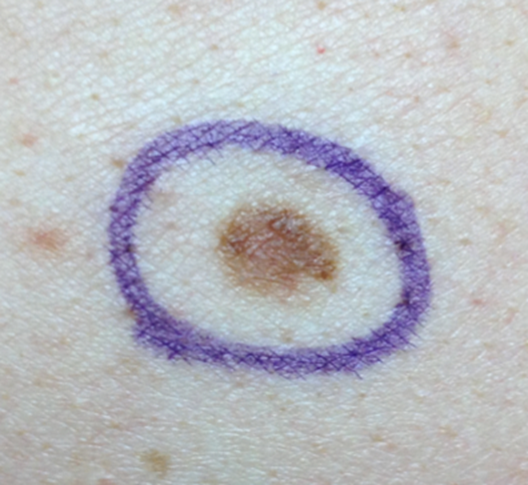
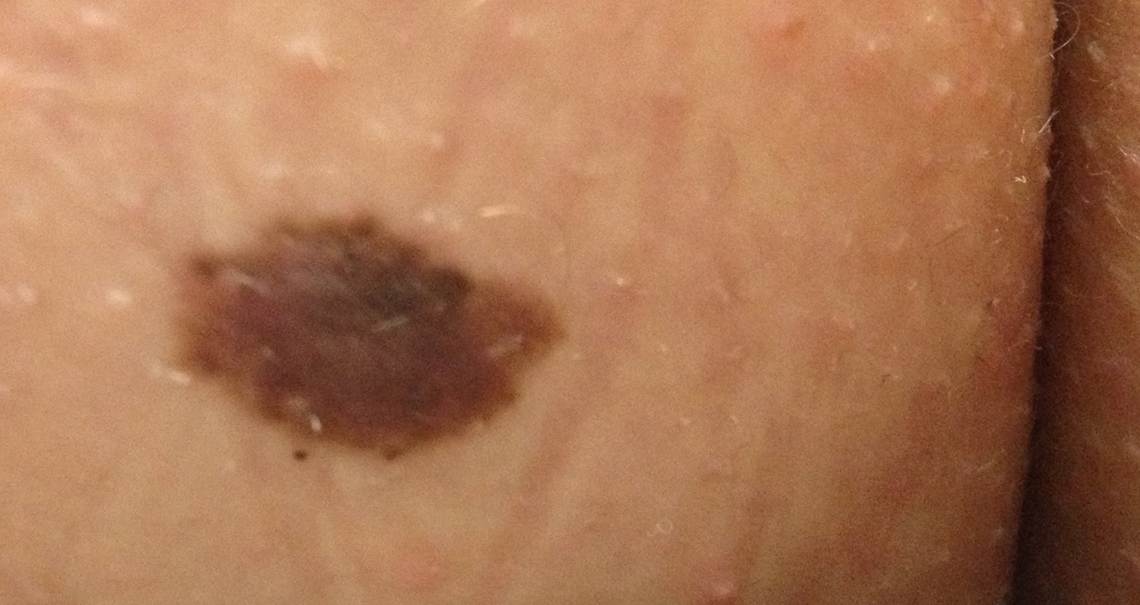
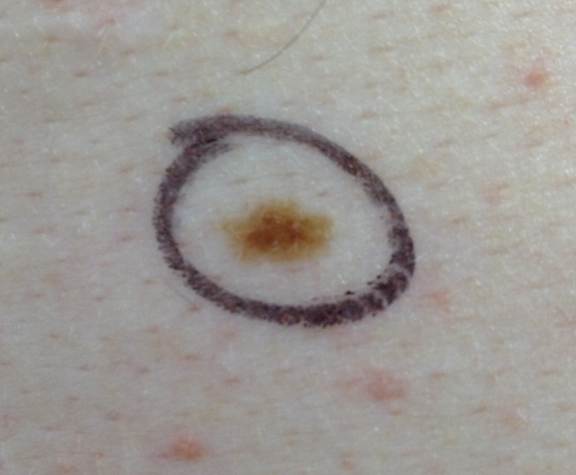
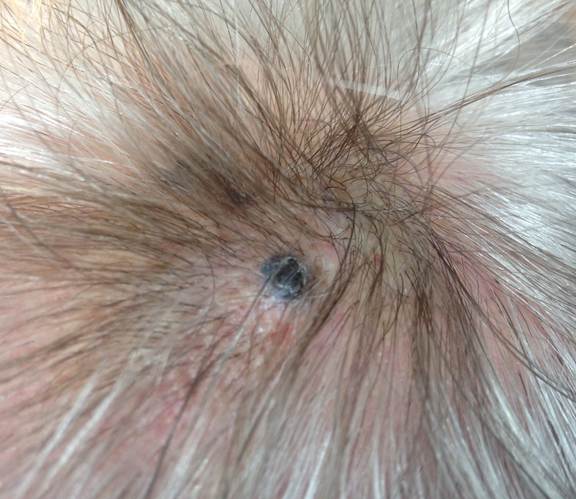
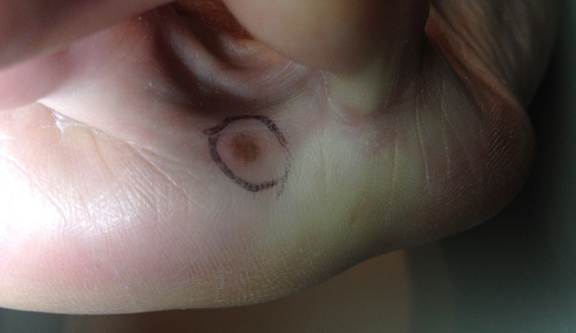
Following are photos of actual atypical moles.
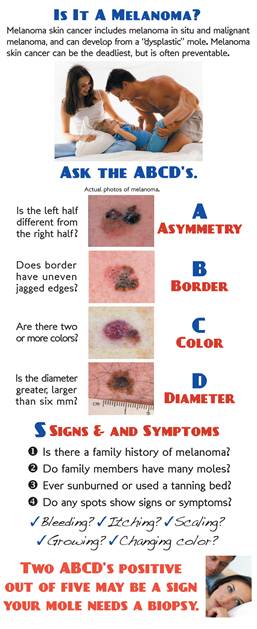
Photos also illustrate the “ABCD’s of Melanoma Detection,” which are: A – Asymmetrical. Dysplastic nevi tend to be asymmetrical. If the lesion were folded in half, the two parts would not match. B – Border irregular. The borders tend to be poorly defined or have a fried-egg appearance. C – Color varies. An atypical nevus tends to have more than one visible color. D – Diameter. While melanomas are usually greater than 6 millimeters (size of a pencil eraser) in diameter when diagnosed, they can be smaller. If you notice a mole different from others, or which changes, itches, or bleeds even if it is smaller than 6 millimeters, you should see a dermatologist. S- Signs & Sympyoms. A mole or skin lesion that looks different from the rest or is changing in size, shape or color. If you have a mole that has any of the ABCD’s or looks like any of those shown in these photos, it may be a dysplastic nevus and should be examined by a dermatologist.
|
|
|